A wind turbine recipe book
Inches and AWG edition for North American readers.

"Your book on Wind Turbine Recipe Book was in the mail box and as soon
as it was in my hands was reading in on the way back into the
house.
Lot better info on how to make the blades.
Your progress in how to make the frame work simple but yet strong shows
in this book."
Sample page below
Buy it here
Cost to buy direct from me (including shipping anywhere in the
world) is roughly US$ 23 including shipping.
A Wind Turbine Recipe Book
This is the latest edition of my 'axial flux windmill plans' as used in
the courses I teach worldwide. The Recipe Book replaces my older
plans 'How to Build a Wind Turbine' (2005). During 2008 the
Recipe book was only available in metric units but now a new 'English
Units' edition is available that is written specifically for North
American
readers who prefer to use Inches and AWG sizes for wire. It is
based on the use of neodymium magnets sized 2" x 1" x 1/2" as available
widely in North America. Since then I have been actively updating
and improving the details so the latest edition at the time of writing
is late 2010.
The Recipe Book is a much better structured document than the older
2005 plans. Rather than evolving 'organically' it is carefully
planned to include six different sizes of turbines. Each section
offers general advice combined with specific dimensions and diagrams
for
each of these six sizes and a range of operating voltages.
I anticipate that there will be demand for the metric version in many
countries world wide, because metric units of measure are actually
easier to use, and many people do understand fractions of inches and
AWG wire sizes. I expect that there will be some ongoing demand
for my older 2005 plans which contain many interesting ideas that I now
consider obsolete, and work in both systems of measure. But the
2009 Recipe Books represent my latest ideas for the simplest and most
effective way to produce small wind turbines.
CONTENTS
Choosing what to do 4
Be safe! 4
How big? 4
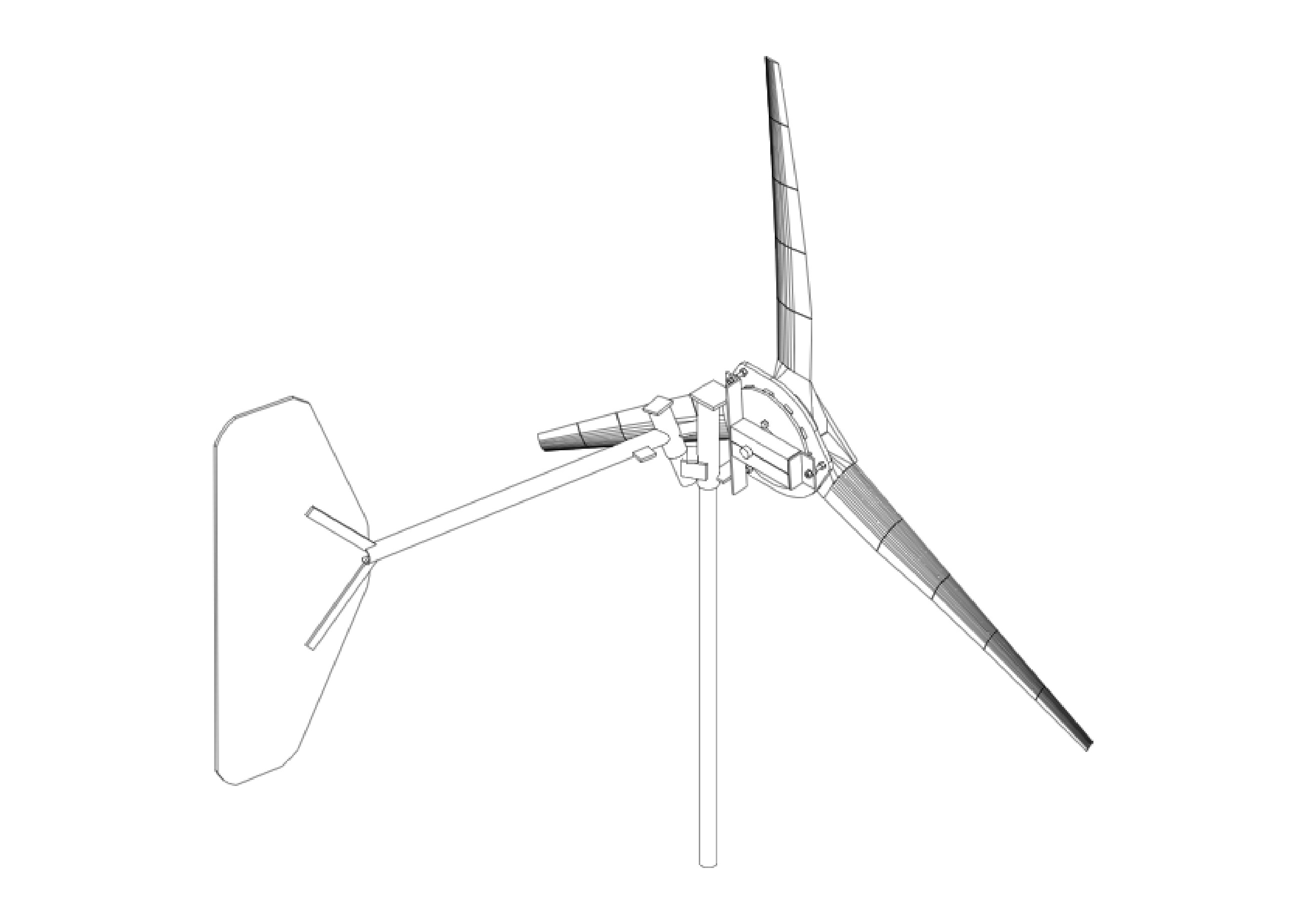
Diagram of a small wind system 4
What can the wind turbine do? 4
Load controllers
5
Choosing battery
voltage 5
Battery types 6
Why some popular ideas are not good
ideas 6
Car alternators
6
Steel cores in the stator
coils 7
Multiple rotors and
stators 7
Vertical axis wind turbines
(VAWTs) 7
Multi blade rotors
8
Rooftop mounting
8
Saving money off the electricity
bill 8
Mounting a wind turbine on a car
to charge the battery 8
Using a centrifugal clutch or
brake to limit speed 9
Building a duct
9
What goes wrong with homebuilt wind
turbines? 9
Useful web pages for more information:
9
Tools 10
Safety etc 10
All-purpose tools
10
For marking and
measuring 10
Electrical 10
Resin preparation
10
Steelwork 10
Woodworking tools
10
Using the tools 11
Cordless drill
11
Screwdriver bits
11
Measurements 11
Vernier calipers
11
Levels 11
Compasses 11
Multimeters 12
Soldering technique
12
Electric Arc welding
12
Cutting steel 13
Drilling 13
Tapping a thread
13
Wood saws 13
Other wood cutting
tools 14
Sandpaper 14
Power tools 14
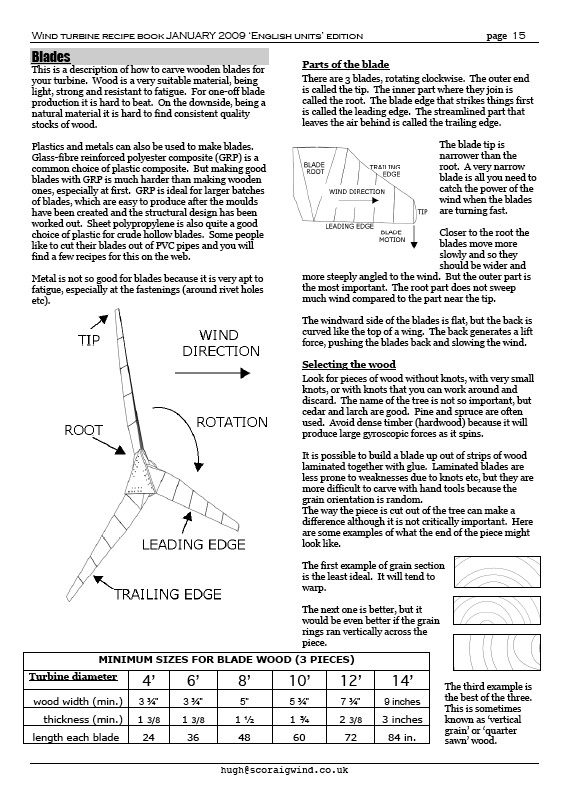
Blades 15
Parts of the blade 15
Selecting the wood 15
The blank shapes 16
The trailing edge line 17
Mark out the shape of the blade at
each of six stations along its length . 17
Carve away wood above the
trailing edge line to create a new face 18
Blade thickness 18
Airfoil shape 19
Hub assembly 20
Cutting the 120 degree angles at
the roots 20
The plywood pieces that sandwich
the blades. 20
Marking out the holes in the
plywood 20
Assembling the blades 21
Balancing 22
Balancing in situ
22
Fine balancing
22
Alternative ways to balance the
blades 22
Balancing on a spike
23
Dynamic balance
23
Painting and finishing 23
Mechanics 24
The yaw bearing 24
The alternator 24
Choosing a hub
24
The magnet rotor
disks 25
Alternator frame
26
Mounting the alternator to the
yaw bearing 27
3600 and 4200
turbines 29
The tail 30
The inclined hinge
30
Tail boom 31
Tail stops 32
Electrics 34
Energy conversion 34
Choosing wire size and number of
turns per coil 34
Stator wiring
connections 35
Three-phase stators
35
Battery charging with
DC 36
The coils 36
12-volt stators marked
* 36
Making the coil
winder 37
Winding the coils
38
Connecting the coils
38
12-volt stators
39
The moulds 39
The stator mould
39
The 1200 stator mould
41
The magnet rotor
mould 41
The magnet positioning
jig 42
Resin casting 43
Casting the stator
43
Casting the magnet
rotor(s) 45
Alternator assembly and testing 46
Rotor mounting
options 46
Rotor mounting studs
47
Assembly 47
12-volt turbine
rectifiers 48
Testing the
alternator 48
Installation 49
Wiring the batteries
49
The rectifier and
brake 49
Meters 50
Controller 50
Inverter 50
Commissioning the turbine 50
Guyed towers 51
Wiring the tower 51
Guyed tower pipe sizes 51
Guy anchors 52
Lifting the tower 53
Taller towers 53
Adjusting the guys
53
Alternator design 54
Matching the blades 54
Tip speed ratio (lambda
l) 54
Calculating the blade rotor
rpm 54
Blade power 54
Calculating the output voltage
vs. speed 54
Wire sizes and power losses 55
Size of wire to use
55
Coil resistance
56
Stator resistance
56
Current and power
loss 57
Rectifier loss 57
Efficiency 57
Windspeed 57
Stator cooling 57
Estimating the rpm 57
Blade speed at full
power 58
Exploring some design factors 59
Magnet spacing
59
The effects of speed
59
The effects of system voltage on
efficiency 59
Varying the voltage with the
speed 59
High voltage
transmission 59
Glossary 60
LIST OF USEFUL SUPPLIERS 62
MATERIALS REQUIRED FOR BUILDING THE WIND TURBINES 63